Firegex tests
GO BACK
Tests are a quick and dirty way to check if your modification to the backend code dind't break anything.
Running all the tests
If you are working on the same machine firegex is running on, you can just run run_tests.sh
$ ./run_tests.sh
It will automatically perform a general API test, Netfilter and Proxy Regex test. You can also run tests manually:
$ ./api_test.py -h
usage: api_test.py [-h] [--address ADDRESS] --password PASSWORD
$ ./nf_test.py -h
usage: nf_test.py [-h] [--address ADDRESS] --password PASSWORD [--service_name SERVICE_NAME] [--port PORT]
[--ipv6] [--proto {tcp,udp}]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--address ADDRESS, -a ADDRESS
Address of firegex backend
--password PASSWORD, -p PASSWORD
Firegex password
--service_name SERVICE_NAME, -n SERVICE_NAME
Name of the test service
--port PORT, -P PORT Port of the test service
--ipv6, -6 Test Ipv6
--proto {tcp,udp}, -m {tcp,udp}
Select the protocol
$ ./px_test.py -h
usage: px_test.py [-h] [--address ADDRESS] --password PASSWORD [--service_name SERVICE_NAME] [--port PORT]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--address ADDRESS, -a ADDRESS
Address of firegex backend
--password PASSWORD, -p PASSWORD
Firegex password
--service_name SERVICE_NAME, -n SERVICE_NAME
Name of the test service
--port PORT, -P PORT Port of the test service
Running a Benchmark
./benchmark.py
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--address ADDRESS, -a ADDRESS
Address of firegex backend
--port PORT, -P PORT Port of the Benchmark service
--internal-port INTERNAL_PORT, -I INTERNAL_PORT
Internal port of the Benchmark service
--service-name SERVICE_NAME, -n SERVICE_NAME
Name of the Benchmark service
--password PASSWORD, -p PASSWORD
Firegex password
--num-of-regexes NUM_OF_REGEXES, -r NUM_OF_REGEXES
Number of regexes to benchmark with
--duration DURATION, -d DURATION
Duration of the Benchmark in seconds
--output-file OUTPUT_FILE, -o OUTPUT_FILE
Output results csv file
--num-of-streams NUM_OF_STREAMS, -s NUM_OF_STREAMS
Output results csv file
--mode {netfilter,proxy}, -m {netfilter,proxy}
Type of filtering
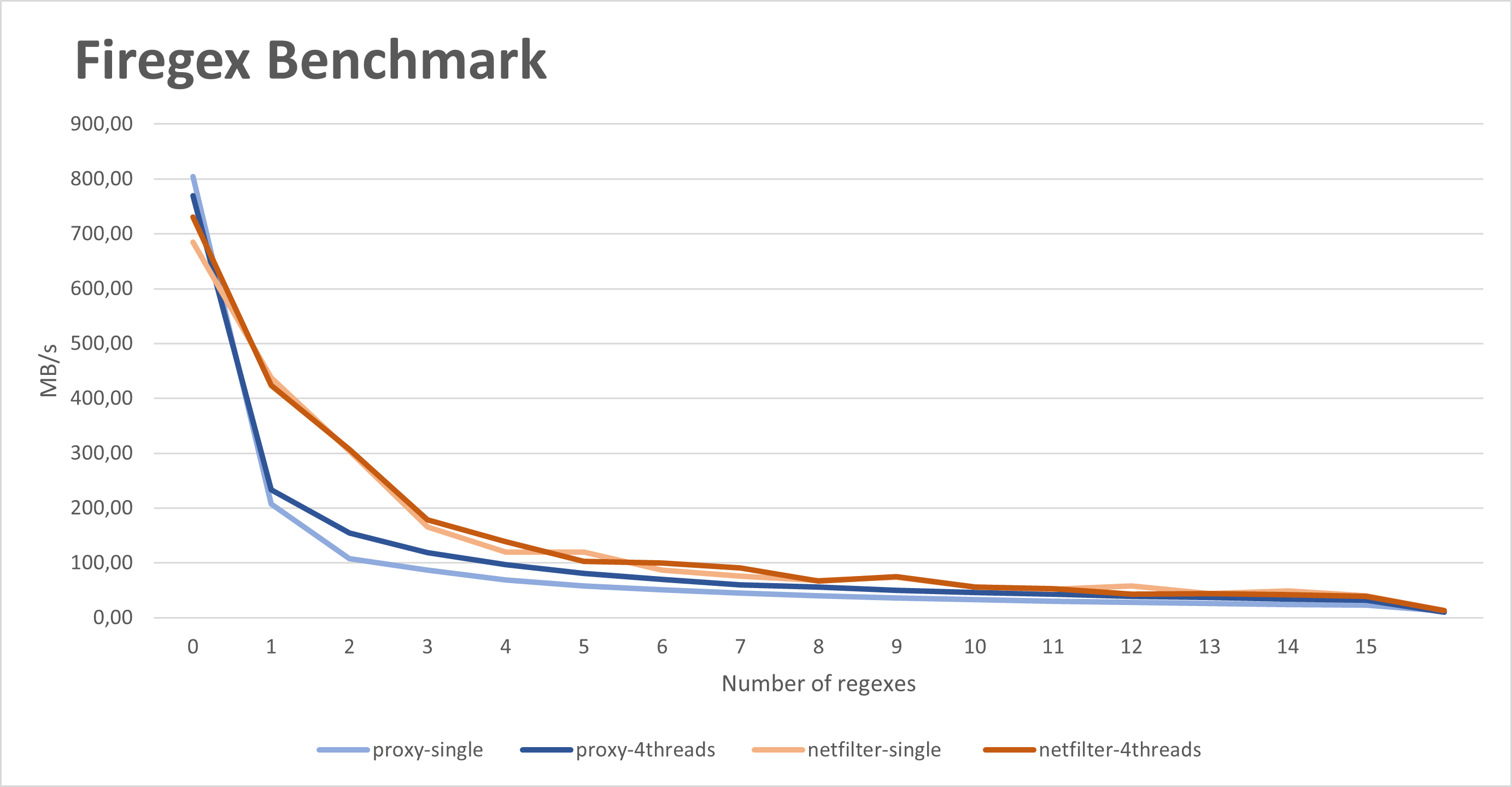
Benchmarks let you evaluate the performance of the filters. You can run one by typing in a shell test.py -p FIREGEX_PASSWORD -r NUM_OF_REGEX -d BENCHMARK_DURATION -m proxy to benchmark the Proxy based regex filter, or -m netfilter to benchmark the Netfilter based regex filtering.
It uses iperf3 to benchmark the throughput in MB/s of the server, both with filters, without filters, and for each new added regex. It will automatically add a new random regex untill it has reached NUM_OF_REGEX specified in the arguments.
You will find a new benchmark.csv file containg the results.
Firegex Performance Results
The test was performed on:
- Bedrock Linux 0.7.27 Poki x86_64
- Intel i5-7200U (4) @ 3.100GHz
- 8GB RAM DDR4 2133 MT/s
Command: ./benchmark.py -p testpassword -r 50 -d 1 -s 60